Everything must be made as simple as possible. But not simpler.
—Albert Einstein
Large Solution SAFe
Large Solution SAFe describes additional roles, practices, and guidance to build and evolve the world’s largest applications, networks, and cyber-physical systems.Large Solution SAFe (Figure 1) configuration includes the following constructs:
- The Essential SAFe configuration
- An additional competency, Enterprise Solution Delivery that describes how to apply Lean-Agile principles and practices to the specification, development, deployment, operation, and evolution of the world’s largest and most sophisticated software applications, networks, and cyber-physical systems.
- The large solution level roles, artifacts, and events
- The full spanning palette
- A connection to the Enterprise or Government entity the solution supports
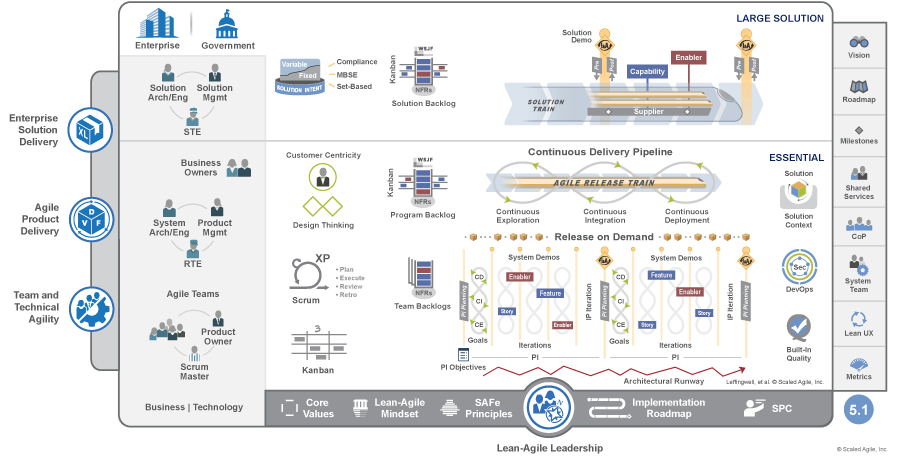
This configuration includes a stronger focus on capturing requirements in the Solution Intent, coordinating multiple Agile Release Trains (ARTs) and Suppliers, and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
Details
Large Solution SAFe is meant for enterprises that face the biggest challenges—building large-scale solutions that are beyond the scope of a single ART to develop. Building these solutions requires additional roles, artifacts, events, and coordination.
The remainder of this article describes the highlights, roles, events, and artifacts presented in the large solution level (Figure 2).
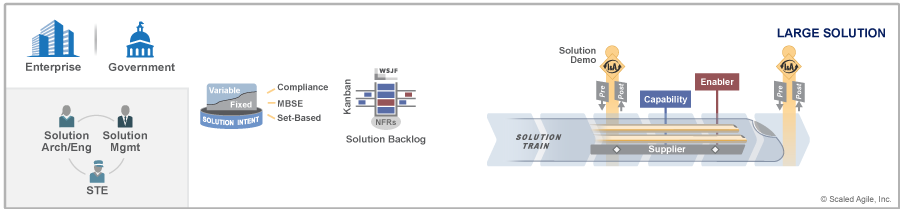
The Solution Train is the organizational vehicle that coordinates the efforts of multiple ARTs and suppliers to deliver the world’s largest and most complex systems. The value delivered by Solution Trains can range from core banking applications in global financial institutions to jet fighters and satellite systems. Lean Enterprises that build these systems-of-systems require abilities, principles, and practices beyond those followed by a single ART. For further discussion and a set of best practices for building large solutions read the Enterprise Solution Delivery competency article.
Large Solution Highlights
Below are the highlights of the Large Solution level:
- Solution Train – The solution train is the key organizational element of the Large Solution SAFe and aligns the people and the work towards a common solution vision, mission, and backlog.
- Solution Intent – Solution intent is a repository for current and future solution behaviors, which can be used to support verification, validation, and Compliance. Solution intent is also used to extend Built-In Quality practices with systems engineering disciplines, including Set-Based Design, Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE), Compliance, and Agile Architecture.
- Solution Kanban – Solution Kanban is a method used to visualize and manage the flow of business and enabler capabilities from ideation to analysis, implementation, and release.
- Spanning Palette – Includes the full spanning palette and all its elements.
Roles
The Large Solution SAFe roles help coordinate multiple ARTs and suppliers and provide the necessary cross-ART coordination and governance:
- Solution Architect/Engineering – The Solution Architect/Engineer represents an individual or small team that defines a common technical and architectural vision for the solution under development.
- Solution Management – Solution management is the content authority for Large Solution SAFe. They work with customers to understand their needs, create the solution vision and roadmap, define requirements (capabilities and enablers), and guide work through the solution Kanban.
- Solution Train Engineer (STE) – The Solution Train Engineer is a servant leader and coach who facilitates and guides the work of all ARTs and suppliers.
- Supplier – Suppliers are an internal or external organization that develops and delivers components, subsystems, or services, which help Solution Trains deliver solutions to customers.
- Shared Services – Shared services represents the specialty roles, people, and services required for the success of an Agile Release Train (ART) or Solution Train, but that cannot be dedicated full-time.
- Communities of Practice (CoP) – CoPs are organized groups of people who have a common interest in a specific technical or business domain who regularly share information, improve their skills, and actively work on advancing the general knowledge of the domain.
Events
Large Solution SAFe uses three major activities to help coordinate multiple ARTs and suppliers:
- Pre- and Post-PI Planning – Pre- and post-PI Planning are used to prepare for, and follow up after, Program Increment (PI) Planning for ARTs and suppliers in a Solution Train.
- Solution Demo – The solution demo shows the results of all the development efforts from multiple ARTs—along with the contributions from suppliers—are integrated, evaluated, and made visible to customers and other stakeholders.
- Inspect & Adapt (I&A) – Inspect & adapt is a significant event where the current state of the integrated solution across all ARTs is demonstrated and evaluated. Solution Train stakeholders then reflect and identify improvement backlog items via a structured problem-solving workshop.
Artifacts
The following Large Solution SAFe artifacts help coordinate multiple ARTs and suppliers:
- Capabilities – Capabilities are a higher-level solution behavior that typically spans multiple ARTs. They are sized and split into multiple features so that they can be implemented in a single PI.
- Enabler Capabilities– Enabler capabilities support the activities needed to extend the Architectural Runway to provide future business functionality and include exploration, architecture, infrastructure, and compliance.
- Solution Epics – Solution Epics are epics implemented by a single Solution Train.
- Nonfunctional Requirements (NFRs) – NFRs define system attributes such as security, reliability, performance, maintainability, scalability, and usability. These are incorporated in solution intent.
- Solution Backlog – Solution Backlog is the holding area for upcoming capabilities and enablers, each of which can span multiple ARTs and are intended to advance the solution and build its architectural runway.
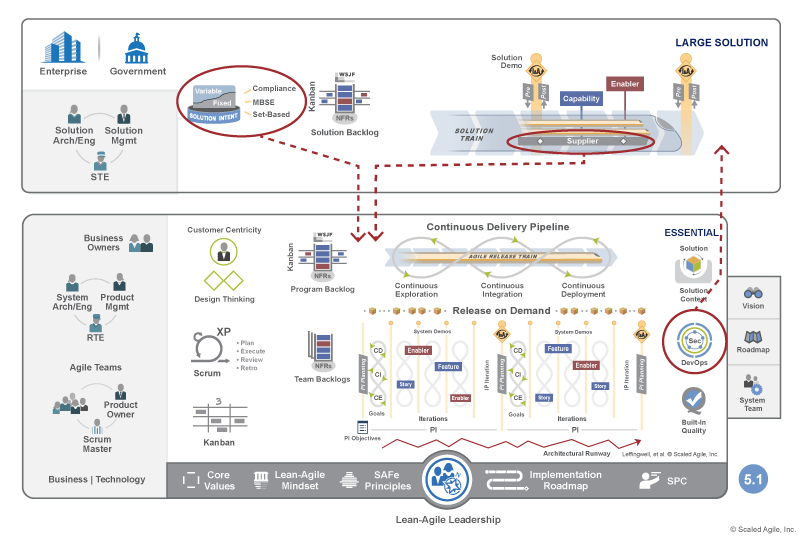
Apply SAFe Elements to Other Configurations
SAFe introduces a number of unique elements in the different configurations. Generally, any SAFe element may be applied to any SAFe configuration. For example, a single ART building a medical device of modest scale will likely have one or more suppliers and a solution intent to manage compliance. Or DevOps could be used by a solution train building a LIDAR system for autonomous vehicles. This is part of SAFe’s scalability and versatility (Figure 4).
Last update: 10 February 2021


